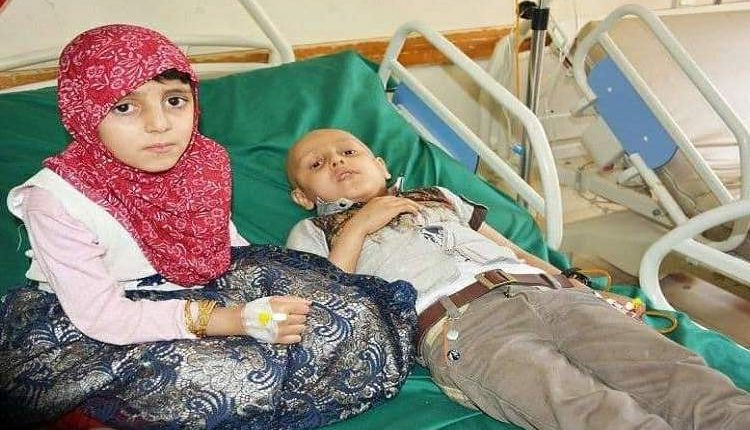
30% Of Yemen’s Children Diagnosed With Leukemia At Risk Of Death Due Closure Of Sanaa Airport
Head of the Pediatric Leukemia Center confirmed that the center lacks supportive drugs and is unable to fully perform bone marrow transplants.
“We treat children with leukemia amid sensitive circumstances as a result of the acute shortage of the high-quality vital, supportive and chemical medicines,” Dr. Abdul Rahman Al-Hadi told Al-Masirah TV.
He pointed out that the shortage of medicines for leukemia patients is due to the reluctance of some pharmaceutical companies to import them and the prevention of their entering through the Ministry of Health by the US-Saudi aggression.
He pointed out that more than 30% of children diagnosed with leukemia need to travel for treatment abroad and are at risk of death due to the closure of Sanaa International Airport.
Al-Hadi added that “the number of pediatric leukemia patients in the center in the capital, Sanaa, has reached nearly 1,300, and we have witnessed a significant increase in the number of patients during the past five years”. He explained that the center receives large numbers of children’s leukemia cases from all over the country, at a rate of two to three new cases per week.
A year ago, the center revealed an increase in cases of leukemia patients among children from 300 to 700 cases, as a result of the US-Saudi use of internationally prohibited weapons, including the airstrikes in Attan and Naqum. The airstrikes have resulted in the injury of a thousand children in the rest of the provinces as well.
The director of the center, Dr. Abd Al-Rahman Al-Hadi, said that since its opening in 2014, the center has received about “1000” cases, stressing that 30% of the cases died as a result of their delay in treatment and also as a result of the blockade that prevented them from receiving treatment abroad.
According to Al-Hadi, the Leukemia Treatment Center in Sanaa suffers from tremendous pressure that exceeds its capacity because it is the only specialized center in Yemen, as the large numbers of patients coming from different provinces exceed the available capacity and medical supplies.