At least 10 million children face severe drought in the Horn of Africa – UNICEF
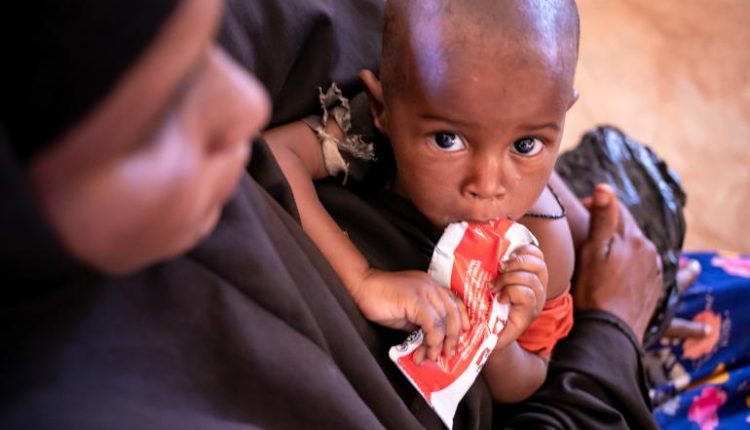
The number of children facing severe drought conditions across the Horn of Africa has increased by more than 40 per cent in the space of two months, warns UNICEF. Between February and April, the number of children facing the impact of drought including acute hunger, malnutrition and thirst increased from 7.25 million to at least 10 million.
UNICEF has revised its emergency appeal from $119 million to nearly $250 million to reflect the growing need across the region. Only 20 per cent is funded.
More than 1.7 million children across Ethiopia, Kenya and Somalia require urgent treatment for severe acute malnutrition. If rains fail in the coming weeks, this figure will rise to 2 million.
“If we don’t act now we will see an avalanche of child deaths in a matter of weeks,” says Mohamed M. Fall, UNICEF.
Regional Director for Eastern and Southern Africa. “Famine is just around the corner.”
The climate-induced emergency across the Horn of Africa is the worst drought the region has seen in 40 years. Three consecutive dry seasons have driven hundreds of thousands of people from their homes, killed vast swathes of livestock and crops, fuelled malnutrition and increased the risk of disease. In Somalia more than 81,000 people are at risk of famine by the end of June if a fourth consecutive rainy season fails, food prices continue to rise sharply, and humanitarian assistance is not stepped up.